Posted in Blog, Facilitation, Innovation, Virtual Facilitation by Jo North
Facilitate a Customer Journey Mapping Workshop that Gets Great Results
The purpose of this article is to help you to:
- Discover great ways to facilitate a customer journey mapping workshop and create insightful, actionable before and after customer journey maps with my step-by-step guide.
- Learn the fundamentals of customer journey mapping and add it to your business tools to improve your organization’s understanding of the customers’ perspective.
- Find out why a customer journey mapping workshop is important for creating a better customer experience and meeting important business needs.
- Improve your knowledge of customer journey mapping and create a clearer understanding of your customers with this powerful tool.

Contents
- What is Customer Journey Mapping?
- What is a Customer Journey Mapping Workshop?
- Overview of the Key Steps to Creating a Customer Journey Map
- Why Facilitate a Customer Journey Mapping Workshop?
- Real Examples of Customer Journey Maps
- Preparation for your Customer Journey Mapping Workshop
- Co-creating a Customer Journey Map with Real Customers
- Customer Journey Mapping Workshop Agenda
- How to Create an Engaging, Productive and Fun Customer Journey Mapping Workshop
- Validating Your New Customer Journey
- Examples of Customer Journey Mapping Software Tools
- Some Useful References and Resources
What is Customer Journey Mapping?
Customer journey mapping is a powerful tool that businesses can use to understand and improve their customer experience. It involves creating a visual representation of every step that a customer takes when interacting with a brand, from initial awareness through to post-purchase activities.
The purpose of customer journey mapping is to gain insights into customer behavior, pain points, and motivations.
By understanding these factors, businesses can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to enhance the customer experience.
Customer journey maps are one of the most powerful business tools available for identifying ways to achieve purposeful and profitable customer-centric innovation and growth. Click To TweetWhat is a Customer Journey Mapping Workshop?
Simply put, a customer journey mapping workshop is a collaborative process where team members work together to create a visual representation of a customer’s experience with a business.
By identifying the different touchpoints a customer has with your business, you can better understand their needs, pain points, and opportunities for improvement.
The ultimate goal of the workshop is to create a better customer experience and meet important business needs.
Overview of the Key Steps to Creating a Customer Journey Map
The process of creating a customer journey map typically involves the following steps:
- Define the stages of the customer journey: The first step is to identify the key stages that a customer goes through when interacting with the brand. This might include awareness, consideration, purchase, and post-purchase activities.
- Gather data: Next, businesses need to gather data about customer behavior at each stage of the journey. This might include surveys, interviews, customer feedback, and analytics data.
- Map the journey: Once the data has been gathered, it’s time to create a visual representation of the customer journey. This might be done using a flowchart or a series of diagrams that illustrate the key touchpoints and interactions that a customer has with the brand.
- Identify customers’ pain points and opportunities: The next step is to analyze the customer journey map and identify areas where the customer experience could be improved. This might include pain points where customers are experiencing frustration or dissatisfaction, as well as opportunities to enhance the customer experience.
- Create a new, target state journey map: Using insights from identification of pain points and opportunities, create a new plan that elevates the user experience and will help to achieve your business innovation and growth objectives.
- Develop a plan: Finally, develop a plan to move from the current customer journey map to the new, target one. This might involve making changes to the product or service, improving customer service, or developing new marketing strategies.
Why Facilitate a Customer Journey Mapping Workshop?
A customer journey mapping workshop is a powerful way to create a better customer experience and meet important business needs. By using different perspectives, identifying pain points, and creating a new customer journey, you can improve the entire map of the customer journey.
Whether you run an in-person or online workshop, a thorough and collaborative process can help you gain a clearer understanding of your customers and create a better customer experience.
Real Examples of Customer Journey Maps
To inspire you and your business, here are three examples of real customer journey mapping from a variety of industries and places around the world:
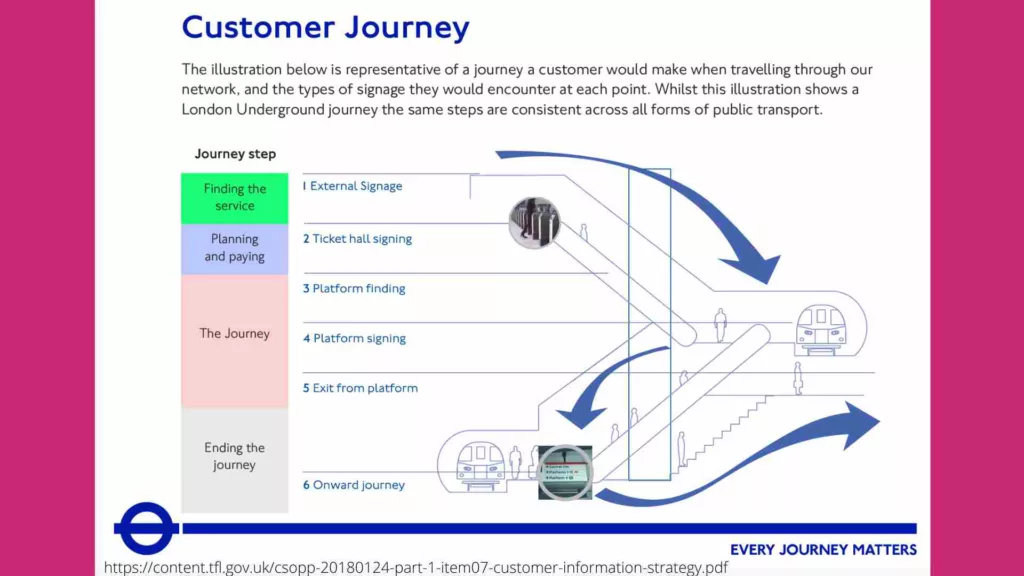
1. Transport for London
Transport for London (TfL) used customer journey mapping to identify pain points in the customer experience of using public transport in London. By mapping the journey from planning a journey to arriving at the destination, TfL was able to identify areas where customers were experiencing frustration and develop strategies to improve the customer experience.
2. IKEA
IKEA used customer journey mapping to understand the customer experience of buying and assembling furniture. By mapping the journey from research and planning to assembly and post-purchase, IKEA was able to identify pain points and develop new products and services to address these issues, such as online planning tools and assembly services.
Ikea is also well-known for its meticulously planned approach to their internal store layouts, which funnel customers through a deliberate journey amongst room designs and products to inspire customers to buy.
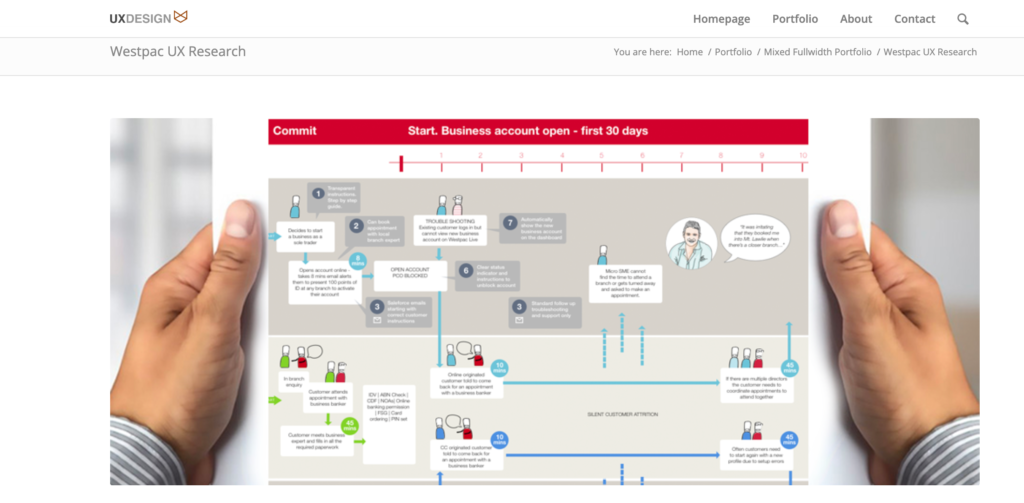
3. Westpac
Westpac, a bank in Australia, used customer journey mapping to identify opportunities for innovation in its mobile banking app. By mapping the customer journey from downloading the app to making a transaction, Westpac was able to identify pain points and develop new features to improve the customer experience, such as mobile check deposits and real-time spending notifications.
There’s also a great example here of how Westpac used customer journey mapping in ux design to explore a particular problem with business banking.
Preparation for your Customer Journey Mapping Workshop
Take these steps to prepare for your customer journey mapping workshop:
- Define the purpose and scope of the workshop: In particular, be specific about which customer segment(s) and which part(s) of the customer journey experience you want to focus on. Keep you scope well-defined – don’t try to cover too much. Your scoping might involve identifying the key touchpoints and interactions that customers have with the business, as well as the goals and outcomes that you want to achieve through the mapping process.
- Gather data: Gather data about customer behavior at each stage of the journey. This might include surveys, interviews, customer feedback, and analytics data.
- Identify the stages of the journey: Based on the data gathered, identify the key stages of the customer journey that customers go through when interacting with your business.
Gather Data for Your Customer Journey Mapping Workshop
To help your workshop participants to develop a comprehensive customer journey map, you’ll need to gather data about customer behavior at each stage of the journey.

Types of Data
Here are some of the key types of data that you need to gather:
Demographic Data
Demographic data includes information such as age, gender, income, education, and location. It helps businesses to understand the characteristics of their target customers and how these characteristics may impact their behavior.
Behavioral Data
Behavioral data includes information about how customers interact with your business at each stage of the journey. This might include website traffic, engagement with marketing materials, and customer service interactions.
Behavioral data helps businesses to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement in the customer journey.
Attitudinal Data
Attitudinal data includes information about customer attitudes, opinions, and beliefs. It helps businesses to understand the motivations and emotions that drive customer behavior.
Competitor Data
Competitor data includes information about your competitors’ products, services, and marketing strategies. It helps businesses to identify areas where they can differentiate themselves and improve the customer experience.
Industry Data
Industry data includes information about industry trends, consumer preferences, and regulatory changes. It helps businesses to stay informed about external factors that may impact the customer experience.
Analytics Data
Analytics data includes data from web analytics tools, social media analytics, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems. It helps businesses to understand customer behavior on a granular level and identify opportunities for improvement.
Customer Feedback
Customer feedback includes information from customer surveys, online reviews, and customer service interactions.
It helps businesses to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement in the customer journey, as well as to understand customer sentiment towards the brand.
Remember the Importance of Customer Emotions
Emotions play a critical role in the customer journey mapping process as they have a significant impact on customer behavior and decision-making. Understanding customer emotions is essential for creating a customer journey map that accurately reflects the customer experience and identifies areas for improvement.
Emotions can be positive or negative and can arise at any stage of the customer journey. For example, a customer may feel excited and hopeful when they first discover a product, frustrated and confused during the purchase process, and satisfied or disappointed after the product arrives.
When creating a customer journey map, it’s essential to consider the emotional experiences that customers have at each touchpoint. This might include identifying moments where customers experience positive emotions, such as delight or joy, as well as moments where they experience negative emotions, such as frustration or anger.
By understanding the emotional experiences of customers, businesses can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to enhance the customer experience. For example, if customers are experiencing frustration during the purchase process, businesses might simplify the process or provide more guidance and support.
Furthermore, emotions are closely tied to customer loyalty and advocacy. Customers who have positive emotional experiences are more likely to become loyal customers and advocates for the brand, while customers who have negative emotional experiences are more likely to switch to a competitor or leave negative feedback.

What to do if you lack data for your customer journey mapping workshop?
If your business does not have access to sufficient data, you may struggle to create an accurate and comprehensive journey map. To overcome this challenge, collect more data through customer feedback surveys, user research, and other data gathering methods. Or invite some trusted, representative and key customers to all or parts of your session.
Co-creating a Customer Journey Map with Real Customers
Co-creating a customer journey map with customers can be an effective way to gain insights into the customer experience and identify areas for improvement.
Here are some ways to co-create a customer journey map with customers:
- Conduct customer workshops: Conducting customer workshops is an effective way to involve customers in the customer journey mapping process. Workshops can include interactive exercises, such as customer journey mapping activities, where customers provide feedback and insights on their experience.
- Conduct customer interviews: Conducting customer interviews can provide valuable insights into customer experiences and emotions throughout the customer journey. This can help to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement in the customer journey.
- Engage customers through social media: Social media can be a powerful tool for engaging customers and involving them in the customer journey mapping process. Businesses can create polls, surveys, and other interactive content to gather feedback and insights from customers.
- Create customer feedback channels: Creating feedback channels, such as online forums or customer feedback forms, can provide customers with an opportunity to share their experiences and provide feedback on the customer journey.
- Use customer journey mapping software: There are several customer journey mapping software available that allow customers to collaborate in real-time with businesses. These tools can facilitate co-creation of the customer journey map by allowing customers to provide feedback and suggestions on the map.
There are some more ideas on how to create a great event for your customers here.
Risks and Benefits of Co-creating with Real Customers
Involving customers in the customer journey mapping process can have both risks and benefits. Here are some of the potential risks and benefits of involving customers in the process, along with strategies for dealing with them:
Benefits:
- Greater customer satisfaction: By involving customers in the process, businesses can gain a better understanding of their needs and preferences, leading to a more satisfying customer experience.
- More accurate insights: Customers can provide valuable insights into their experiences that businesses may not be aware of, leading to more accurate and comprehensive journey maps.
- Enhanced customer engagement: Involving customers in the process can create a sense of ownership and investment in the customer journey, leading to greater engagement and loyalty.
- Greater innovation: By involving customers in the process, businesses can identify new ideas and opportunities for innovation that they may not have considered otherwise.
Risks:
- Complexity: Involving customers in the process can make it more complex and time-consuming, potentially slowing down the journey mapping process.
- Biased feedback: Customers may provide biased or incomplete feedback, leading to inaccurate or incomplete journey maps.
- Confidentiality concerns: Customers may be hesitant to provide feedback if they are concerned about the confidentiality of their information.
- Cost: Involving customers in the process can be costly, particularly if businesses need to offer incentives or compensation for their time and participation.
Strategies for dealing with risks:
- Manage complexity: To manage the complexity of involving customers in the process, businesses can break the process down into smaller, more manageable steps and use technology to streamline communication and collaboration.
- Address bias: To address bias in customer feedback, businesses can use a variety of feedback methods and gather feedback from a diverse group of customers to ensure that multiple perspectives are represented.
- Ensure confidentiality: To address confidentiality concerns, businesses can communicate clearly with customers about how their feedback will be used and stored, and ensure that all customer data is stored securely.
- Control costs: To manage costs, businesses can consider offering non-monetary incentives, such as recognition or exclusive access to new products or services.
Customer Journey Mapping Workshop Agenda
Introduction:
- Welcome and introductions
- Overview of the purpose and scope of the workshop
Activity 1: Persona Creation
- Define customer personas based on demographic and behavioral data
- Get clear on the personas’ “jobs to be done”. These are what the customer really aims to accomplish when interacting with your business.
- Identify the characteristics, goals, and pain points of each persona
Activity 2: Creating a Customer Journey Map
- Identify the stages of the customer journey based on the data gathered
- Map out the touchpoints and interactions that customers have with the business at each stage of the journey
- Add emotional and behavioral insights to each touchpoint based on the customer feedback and data gathered
Activity 3: Pain Point Analysis
- Analyze the customer journey map to identify areas where the customer experience could be improved
- Identify pain points where customers are experiencing frustration or dissatisfaction, as well as opportunities to enhance the customer experience
Activity 4: Creating a New Customer Journey
Activity 5: Action Planning
- Prioritize actions that need to be taken to improve the customer experience based on the pain points identified
- Develop a plan to address the pain points and opportunities identified in the customer journey map
Conclusion
- Recap of the workshop and key insights gained
- Review of action plan and next steps
Post-Workshop Follow-up
- Share the customer journey map and action plan with the team and stakeholders
- Validate the new customer journey map with real customers
- Implement the action plan and monitor the impact on the customer experience
- Review and update the customer journey map regularly to ensure that it remains relevant and up-to-date
How to Create an Engaging, Productive and Fun Customer Journey Mapping Workshop
Here are some creative elements that you can incorporate into your customer journey mapping workshop to make it even more engaging, productive and fun:
- Role-playing: In this activity, team members take on the role of customers and act out different scenarios to explore the customer journey. This can help to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement in the customer experience. Even better, bring in some real customers for parts of your workshop!
- Visual storytelling: Use visual aids, such as images, videos, or infographics, to tell the story of the customer journey throughout your workshop. This can help to engage team members and provide a deeper understanding of the customer experience.
- Gamification: All the way through your workshop you can use game mechanics, such as points, rewards, and challenges, to make the customer journey mapping process more engaging and fun. This can help to increase team participation and creativity.
- Work in manageable chunks: Customer journeys can be complex and involve multiple touchpoints across different channels. This can make it difficult to create a comprehensive and accurate journey map. To overcome this challenge, make sure that your workshop participants break down the customer journey into smaller, more manageable parts and use multiple maps to cover the entire journey.
There are lots of other useful tips on how to be a great facilitator in my article here.
Introducing the Workshop
At the start of your workshop, set clear ground rules. This means establishing common goals, providing a basic understanding of customer journey mapping, and setting time management guidelines. It’s also important to ensure that all workshop participants, from senior managers to the marketing team, understand the importance of customer satisfaction, customer experience and empathy in the workshop.
To begin the workshop, divide workshop attendees into smaller groups and assign each group a different team to work on. Each team should represent a different target persona, or ideal customer, to ensure that the workshop covers a variety of perspectives. It’s also important to use research data, such as market research or customer interviews, to guide the workshop process.
Activity 1: Persona Creation
Persona creation is a process of creating fictional characters that represent the different types of customers who interact with your business. Personas help businesses to understand the characteristics, goals or “jobs to be done“, and pain points of their target customers, and use this understanding to create products and services that meet their needs.
You could use a template like the one shown in the visual below.

Step-by-step Guide on How to Do Persona Creation
- Gather data: The first step in persona creation is to gather data about your customers. This might include demographic data such as age, gender, income, and education, as well as behavioral data such as purchasing habits, interests, and motivations.
- Identify commonalities: Once you have gathered data, identify the common characteristics that customers share. This might include shared goals, pain points, or behaviors.
- Define your personas: Based on the commonalities identified, define your personas. A persona is a fictional character that represents a specific customer type. Give each persona a name, demographic information, and behavioral information that reflects their characteristics.
- Prioritize personas: Prioritize the personas based on their importance to your business. You may want to focus on personas that represent your primary target audience or personas that represent a segment of your customer base that you want to grow.
- Validate your personas: Validate your personas by testing them against the data that you have gathered. Ensure that each persona accurately reflects the characteristics, goals, and pain points of your target customers.
- Use your personas: Use your personas to guide decision-making across your business. Use them to inform product development, marketing, and customer service strategies that meet the needs of your target customers.
Bonus tip: I encourage people to think about a number of real customers within the same segment that they know well. Also to use key insights about these real people to develop their customer personas for the workshop.
Alternative Persona Creation Activities
Gamification Option
- Divide the team into smaller groups and assign each group a persona and a specific customer journey stage to focus on.
- Give each group a set of cards or tokens, each representing a different touchpoint or interaction that customers have with the business at their assigned stage.
- Explain the rules of the game: Teams must use the cards or tokens to create a customer journey map for their assigned stage, placing the cards or tokens in the order that customers would typically encounter them.
- Each card or token has a point value assigned to it, based on its importance to the customer journey. Teams must strategize and allocate their cards or tokens in a way that maximizes their point value.
- After a set amount of time, have the teams present their customer journey maps and explain their strategy for maximizing point value.
- Award prizes or recognition to the team that earns the most points or develops the most innovative strategy.
Customer Empathy Interviews
Customer empathy interviews are a good option to support this activity. In the session, or as pre-work, teams conduct interviews with customers to gain insights into their experiences and emotions throughout the customer journey. This can help to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement in the customer experience.
It’s a great idea to video record these interviews. They can be shared with colleagues internally.
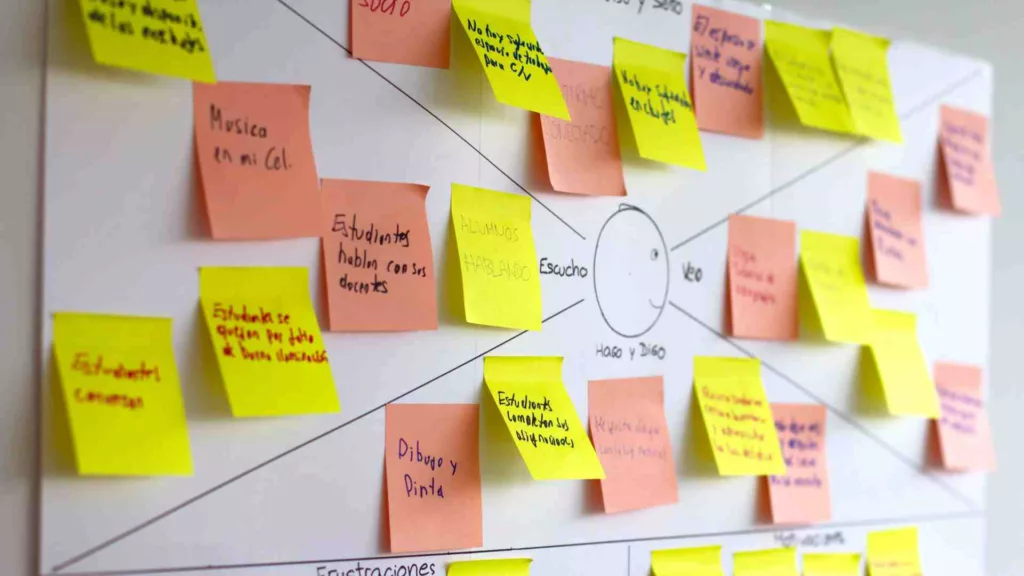

Activity 2: Creating a Customer Journey Map
The first step is to create a user journey map.
Sometimes this is called a “current-state hypothesis map”. This map is a visual representation of the customer journey based on assumptions and hypotheses about the customer experience. It should include all the touchpoints and interactions that customers have with the business using the available data.
It involves creating a visual representation of the customer’s journey, including the key moments, touchpoints, and pain points. You can do this by using sticky notes or an empathy map, a powerful tool for understanding the customer’s perspective.
To create the user journey map, plot the different touchpoints and experiences along a horizontal line that represents the chronological order of the customer journey. Then, use a vertical axis to represent the customer’s emotions and experiences at each touchpoint. This will give your participants a clearer understanding of the customer’s experience and help them to identify areas of opportunity.
Bonus tip: You could ask delegates to create their versions of the current state customer journey map in advance of the workshop, to bring with them and combine with their colleagues’ versions.
Different Types and Styles of Customer Journey Maps
There are several types and styles of customer journey maps, each with their own unique features and benefits. Here’s a detailed list of some of the most common types and styles:
Linear Journey Map
A linear journey map shows the customer journey as a linear progression, with each stage of the journey represented by a sequential step. This is the most common and traditional style of customer journey map.
Non-linear Journey Map
A non-linear journey map represents the customer journey in a non-linear format, such as a diagram or flowchart, that allows the customer to move back and forth between stages as needed. This style is useful for complex customer journeys with multiple touchpoints.
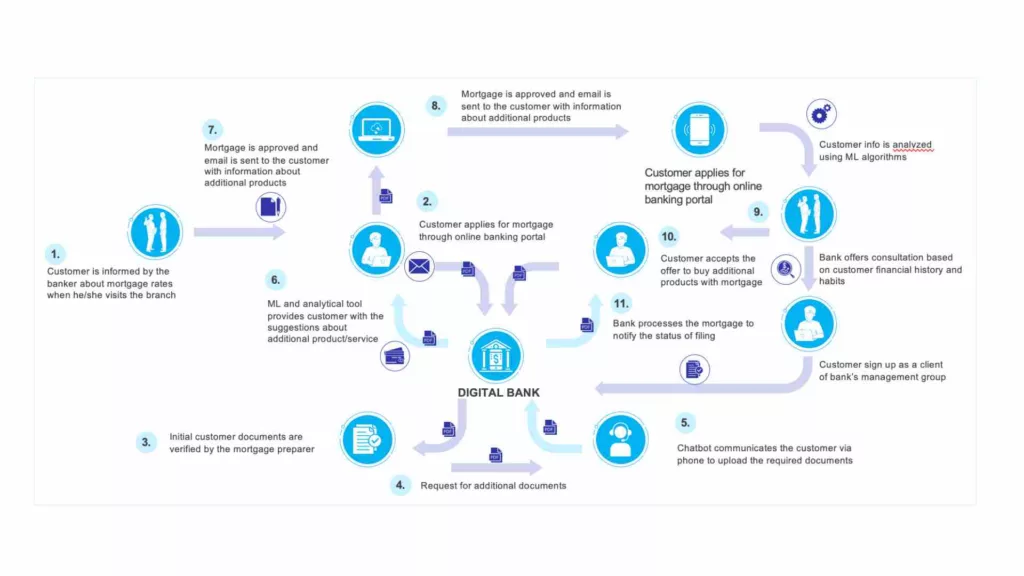
Emotional Journey Map
An emotional journey map focuses on the emotional experiences of customers at each stage of the journey. This style can be used to identify emotional pain points and opportunities for emotional connection with customers.
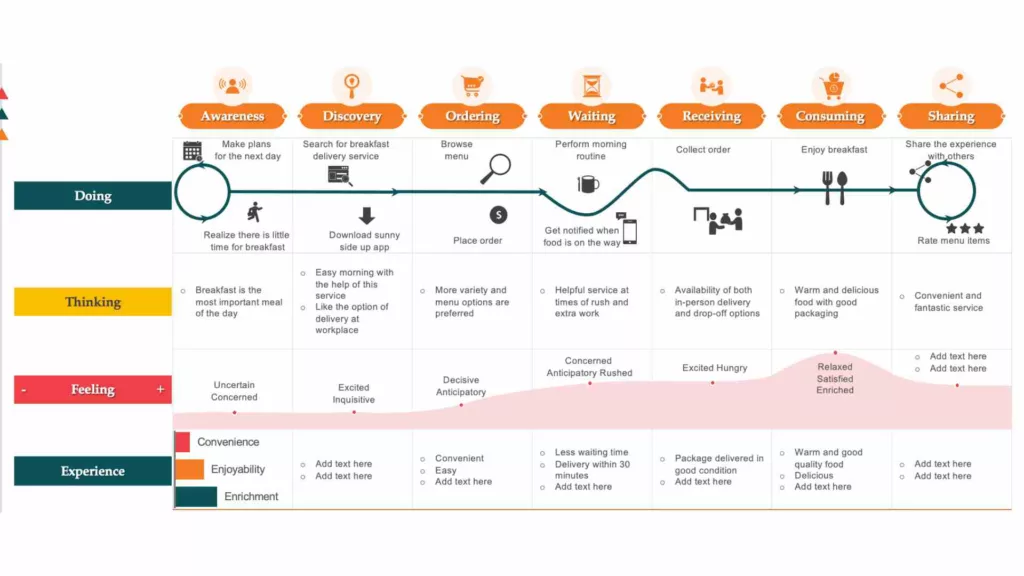
Service Blueprint
A service blueprint is a detailed map that shows the interactions between customers, employees, and processes across the entire service experience. This style is useful for identifying pain points and opportunities for process improvement.
Usually, first-hand interactions with employees in your business are captured as “front of house” or “on stage” experiences. People working “behind the scenes” – such as finance, despatch, marketing (depending on the nature of your business) are also included in the journey experience map to indicate how well the organization is set up to serve the customer.
In addition to employees, physical and virtual touchpoints on the journey are tracked and analyzed.
Moments of Truth
Examining the customer’s interaction with these elements can shed light on the “moments of truth” for your business.
Moments of truth (MoT) are moments when the customer interacts with your brand, product or service, and their experience leads them to create or change their opinion (positively or negatively) about your proposition and business.
Persona-based Journey Map
A persona-based journey map shows the customer journey from the perspective of a specific customer persona. This style is useful for identifying pain points and opportunities to enhance the customer experience for a particular group of customers.
Channel-based Journey Map
A channel-based journey map shows the customer journey for a specific channel or touchpoint, such as a website or mobile app. This style is useful for identifying pain points and opportunities to improve the customer experience for a particular channel.
Hybrid Journey Map
A hybrid journey map combines elements of multiple journey map styles to provide a comprehensive and detailed view of the customer journey. This style is useful for complex customer journeys that involve multiple touch points and interactions.
Bonus Tips
Bear in mind that some of these are overlapping and their features can be combined – e.g. you can create a non-linear, persona-based emotional journey map.
Decide what sort of map you’d like your workshop participants to create in advance of the session.
As long as they stay on track, participants can enhance and shape the format of their map as they work, so allow for some creative freedom within the scope that you set them.
Advanced Tips
A question that facilitators and delegates often ask me is: “how do you do customer journey mapping when your customer swaps between numerous channels in the same journey?”
I wholeheartedly agree that when customers swap between numerous channels in the same journey, it can be challenging to create a traditional linear journey map.
However, there are several approaches you can take to create an effective customer journey map in this scenario.
Multi-channel journey map
A multi-channel journey map shows the customer journey across multiple channels, highlighting the touchpoints and interactions that occur on each channel. This approach can help businesses to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement at each touchpoint.
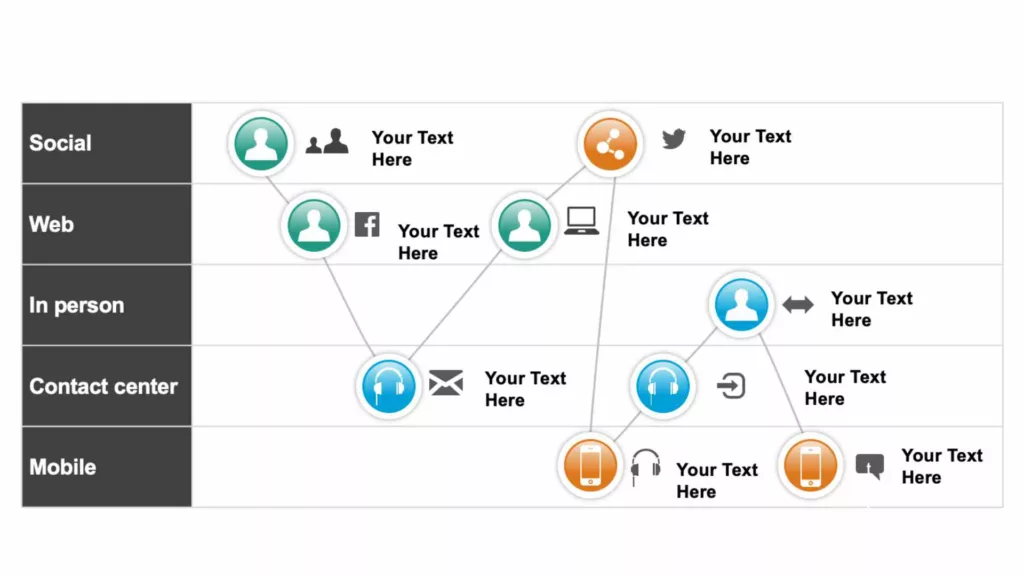
Channel-specific journey maps
Creating channel-specific journey maps for each channel the customer uses can provide a more detailed and targeted view of the customer journey. This approach allows businesses to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement on each channel. They can then develop strategies to improve the overall customer experience.
Journey mapping with customer feedback
Gathering feedback from customers about their journey across multiple channels can provide valuable insights into pain points and areas for improvement. This approach allows businesses to identify customer needs and preferences across different channels and develop strategies to meet these needs.
Activity 3: Pain Point Analysis
A customer pain point refers to a specific problem or challenge that a customer is facing in relation to a product or service. It is a term often used in business and marketing to describe areas where customers are dissatisfied and may be considering a switch to a competitor’s offering. Identifying and addressing customer pain points is a critical aspect of customer experience management and can help businesses improve their products or services to better meet customer needs.
A customer pain point can take many forms. Examples are a difficult user interface, poor customer service, high costs, or low product quality. Identifying these pain points requires careful observation of customer behavior, feedback, and market research. Addressing pain points may involve product redesign, process improvement, or a shift in marketing strategy.
By addressing your customers’ most important pain points better than your competition, you’ll create a distinctive, compelling value proposition.
Make sure participants identify the real customer pain points, not superficial ones.

Identifying Challenges and Opportunities
As you work through the journey mapping process, it’s important to keep the scope of the journey in mind. This means focusing on the entire journey, from the first point of contact to the end point, rather than isolated touchpoints. By taking a comprehensive approach, you can create a better customer experience.
Once you’ve created the user journey map, next identify the biggest challenges and opportunities for improvement. Use the entire team’s expertise and knowledge to identify the biggest pain points and negative experiences. This will help you prioritize which areas need the most attention.
Prioritizing Pain Points
After gathering feedback and refining the map, the next step is to prioritize pain points within the journey. This involves identifying the most critical pain points that have the greatest impact on the customer experience. Prioritizing pain points helps to ensure that resources are focused on the most important issues and that the customer experience is improved in the most impactful way.

Activity 4: Creating a New Customer Journey
The next step is to create a new customer journey, one that takes into account the areas of opportunity you identified earlier. This can be done by brainstorming different ways to improve the customer experience and testing them out to see which works best.
The final step in facilitating a customer journey mapping workshop is to create a future-state vision through sketching activities.
This involves creating a visual representation of the ideal customer experience, based on the feedback and ideas generated during the workshop.
Participants can be asked to sketch their vision of the future-state journey map and share their ideas with the group. This can help to create a shared vision of the ideal customer experience and provide a roadmap for future improvements.

Storytelling Activities for Your Customer Journey Mapping Workshop
I strongly recommend that you consider asking your workshop participants to use storytelling activities to bring their customer journey mapping to life. There are lots of ideas for facilitators in my article here and video below.
Competitive Differentiation
Creating a customer experience that differentiates a business positively from the competition is crucial to attracting and retaining customers. Here are some ways you can prompt and encourage your workshop participants can achieve this:
- Provide personalized experiences: Use customer data to provide personalized experiences that meet the unique needs and preferences of each customer. This can include personalized recommendations, customized products, and personalized communication.
- Create a seamless experience: Ensure that the customer experience is seamless and effortless, with easy navigation and clear communication at every touchpoint. This can include clear product descriptions, simple checkout processes, and responsive customer service.
- Focus on emotion: Focus on creating emotional connections with customers, such as by providing exceptional customer service or by tapping into customer values and beliefs. This can help to build loyalty and differentiate the business from competitors.
- Innovate: Continuously innovate and improve the customer experience, whether through new products or services, new technologies, or new processes. This can help to set the business apart from competitors and provide a unique value proposition.
- Cultivate a strong brand: Develop a strong brand identity and voice that resonates with customers and reflects the values and personality of the business. A strong brand can help to differentiate the business from competitors and create a positive emotional connection with customers.
At the end of this activity, your delegates should have finalized maps of the customer journey that reflect customers’ most important needs.
Activity 5: Action Planning – Next Steps for Your Customer Journey Planning Workshop
Once the team has generated a list of ideas, prioritize and select the most feasible and impactful actions. Use a tool such as a decision matrix. This can help the team evaluate and rank the ideas based on their potential impact and feasibility.
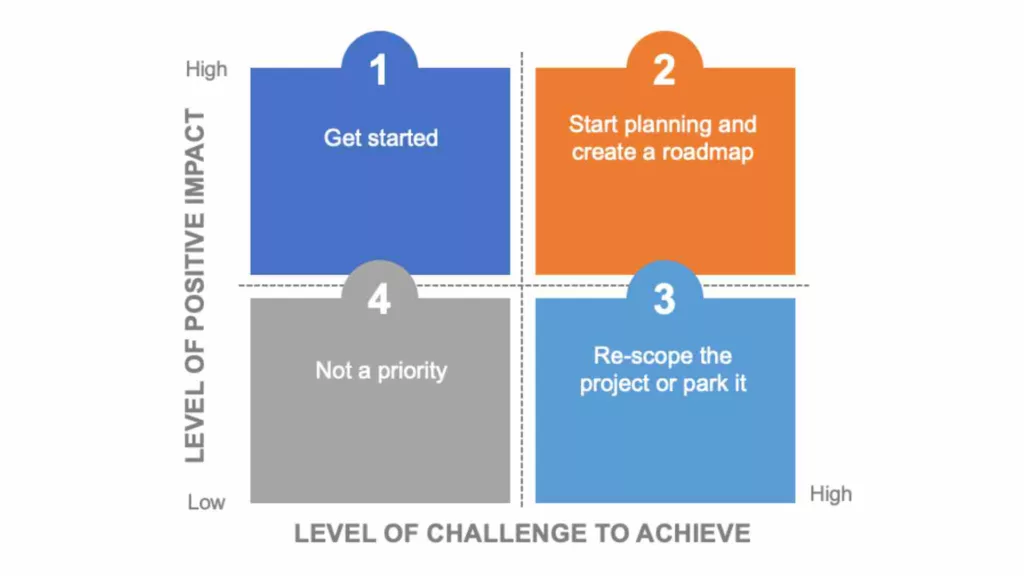
Ask your participants to agree roles and responsibilities. Set realistic timelines and deadlines for each action item. Agree to track progress regularly to ensure that the team is making progress towards their goals and objectives.
Post Customer Journey Mapping Workshop Follow-Up
Share the customer journey map and action plan with the team and stakeholders.
Make sure that the team validates the maps with real customers.
Once the action plan is being implemented, monitor the impact on the customer experience using data.
Don’t stop there. Drive for continuous improvement. Review and update the customer journey map regularly to ensure that it remains relevant and up-to-date
Validating Your New Customer Journey
Validating a customer journey map is an essential step in ensuring that the map accurately reflects the customer experience and identifies areas for improvement.
Here are some ways to validate a customer journey map:
- Review and analyze customer feedback: Reviewing customer feedback, such as surveys, online reviews, and customer service interactions, can help to identify pain points and areas for improvement in the customer journey. Comparing the feedback with the customer journey map can validate or highlight any discrepancies in the map.
- Conduct user testing: User testing involves having customers interact with the business or product and providing feedback on their experience. This can help to validate the customer journey map and identify any issues or opportunities that were not previously identified.
- Analyze web data: Web analytics, such as website traffic and engagement metrics, can help to validate the customer journey map and identify any areas where customers are experiencing issues or dropping off.
- Conduct interviews with customers: Conducting interviews with customers can provide valuable insights into their experiences and emotions throughout the customer journey. This can help to validate the customer journey map and identify any areas for improvement.
- Collaborate with stakeholders: Collaborating with stakeholders, such as marketing, sales, and customer service teams, can help to validate the customer journey map and ensure that it accurately reflects the customer experience. Stakeholders can provide insights and feedback on the map based on their experiences and interactions with customers.
There are lots more creative techniques for validating business ideas in this article here.

Examples of Software Tools for Your Customer Journey Mapping Workshop
There are several software options available that you could use to create, analyze, and improve your customer journey maps.
Here are some examples of customer journey mapping software:
Smaply
Smaply is a customer journey mapping software that allows businesses to create and share customer journey maps. The software includes features such as persona creation, touchpoint mapping, and data visualization.
Touchpoint Dashboard
Touchpoint Dashboard is a customer journey mapping suite of tools that allows businesses to create customer journeys across multiple channels. The tool includes features such as touchpoint analysis, customer persona creation, and data visualization.
UXPressia
UXPressia is a customer journey mapping software that allows businesses to create and share customer journey maps. The tool includes features such as persona creation, touchpoint mapping, and customer feedback analysis.
Canvanizer
Canvanizer is a cloud-based customer journey mapping software that allows businesses to create, collaborate and share customer journey maps. The tool includes features such as persona creation, touchpoint mapping, and data visualization.
Customer Journey Mapping by Creately
Customer Journey Mapping by Creately is a customer journey mapping software that allows businesses to create and share customer journey maps. The software includes features such as touchpoint mapping, customer persona creation, and data visualization.
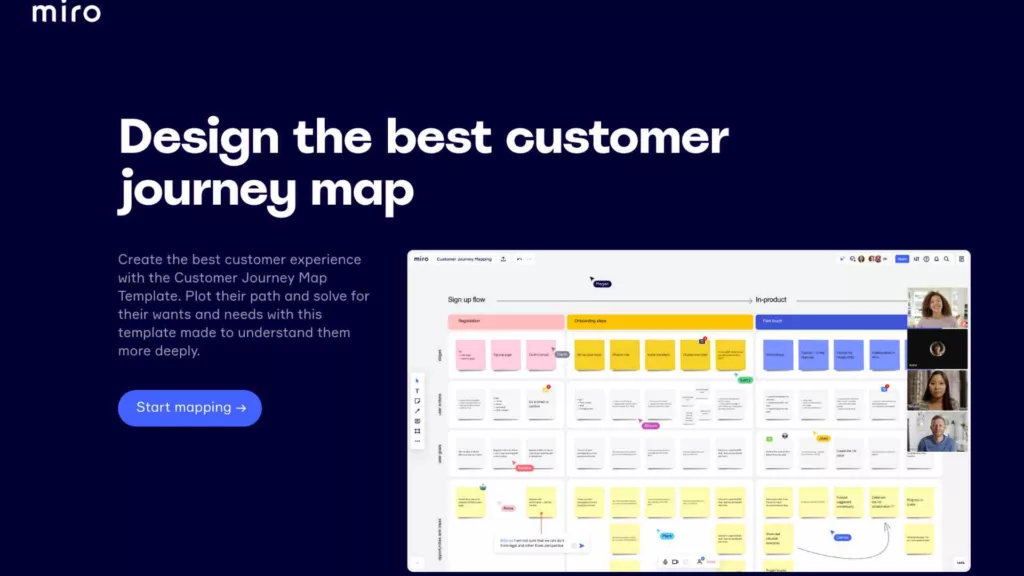
Miro Customer Journey Map Template
Miro Customer Journey Map Template. Your participants can plot customers’ paths and collaborate on solving their wants and needs with Miro’s online workshop template.
These customer journey mapping tools can help you and your business to collaborate and gain insights into customer behavior, pain points, and motivation.

Some Useful References and Resources for Your Customer Journey Mapping Workshop
Harvard Business Review. (2015). The new science of customer emotions. https://hbr.org/2015/11/the-new-science-of-customer-emotions
The Journey Mapping Playbook: A Practical Guide to Preparing, Facilitating and Unlocking the Value of Customer Journey Mapping, by Jerry Angrave
How Hard Is It to Be Your Customer? Using Journey Mapping to Drive Customer Focused Change, by Jim Tincher and Nicole Newton
User Journey Mapping, by Stephanie Walter