Posted in Blog, Facilitation, Innovation by Jo North
Understanding the Power of Knowledge Exchange: A Comprehensive Guide
Knowledge exchange fuels business innovation by facilitating the sharing of ideas, expertise, and best practices. This collaboration accelerates problem-solving, enables cross-industry learning, and sparks new approaches, ultimately driving growth, competitiveness, and long-term success.
This article is a comprehensive guide to understanding the power of knowledge exchange for facilitators in universities, public sector, private sector businesses and third sectors. It defines and explains the terminology, key concepts, structures and processes involved in knowledge exchange activities.
Jump to contents:
- Introduction to Knowledge Exchange
- Why is Knowledge Exchange Important?
- Universities and Knowledge Exchange
- What is a Knowledge Exchange Framework?
- Knowledge Transfer Partnerships and Knowledge Transfer Networks
- Intellectual Property (IP)
- Knowledge Exchange Organizations
- Knowledge Exchange Conferences and Events
- Resources and Literature
Introduction to Knowledge Exchange
Knowledge exchange is crucial for innovation. It facilitates the sharing of ideas, experiences, best practices, and expertise among individuals, teams, and organizations.
It is an essential part of an organization’s knowledge management strategy, taking internal knowledge transfer one step further through external collaborations.
Important Definitions
Definitions and explanations of the terms knowledge management, knowledge transfer, and knowledge exchange are detailed below.
Knowledge Management
Knowledge management (KM) is a multidisciplinary approach to creating, sharing, using, and managing knowledge and creating easier access to information within an organization or a group.
The primary goal of knowledge management is to enhance organizational performance, innovation, and competitive advantage. It achieves this by leveraging the collective knowledge, expertise, and experiences of individuals and teams.
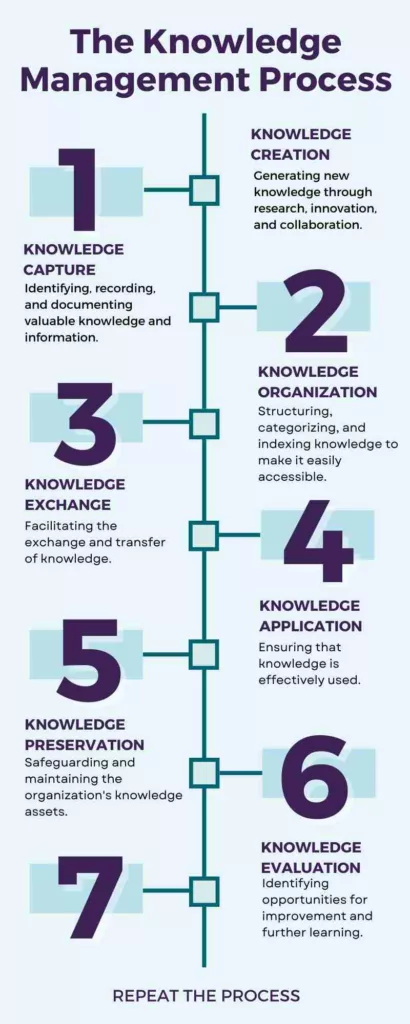
The Knowledge Management Process
Knowledge management involves a range of processes, practices, and technologies, including:
- Knowledge creation: Generating new knowledge through research, innovation, and collaboration.
- Knowledge capture: Identifying, recording, and documenting valuable knowledge and information. This includes tacit knowledge (unwritten, unspoken, and hidden knowledge) and explicit knowledge (formalized and documented knowledge).
- Knowledge organization: Structuring, categorizing, and indexing knowledge to make it easily accessible and retrievable for users.
- Knowledge exchange: Facilitating the exchange and transfer of knowledge among individuals, teams, and departments within the organization. Also with external stakeholders such as partners, customers, and suppliers.
- Knowledge application: Ensuring that knowledge is effectively used to improve decision-making, problem-solving, and processes throughout the organization, in line with good practice.
- Knowledge preservation: Safeguarding and maintaining the organization’s knowledge assets to prevent loss and ensure long-term availability.
- Knowledge evaluation: Assessing the quality, relevance, and impact of knowledge on organizational performance. Identifying opportunities for improvement and further learning.
Supporting Knowledge Management
Knowledge management relies on a combination of organizational culture, processes, and technologies to support these activities.
The success of a knowledge management strategy depends on the organization’s ability to create a culture that values and encourages the sharing and use of knowledge, as well as the implementation of effective systems and tools to support knowledge management processes.
What is Knowledge Exchange?
Knowledge exchange is an important part of a knowledge management strategy. It is the process of sharing knowledge, expertise, and information between individuals, organizations, and communities.
There are several different definitions of knowledge exchange, each of which emphasizes a different aspect of the process. Some of the most common definitions of knowledge exchange include:
- The exchange of ideas, information, and expertise between individuals or organizations for the purpose of mutual learning.
- The transfer of knowledge and skills from one person or organization to another, often with the goal of improving performance or outcomes.
- The process of sharing knowledge and information across disciplinary, cultural, or institutional boundaries, with the goal of facilitating innovation and problem-solving.
- The collective process of generating, sharing, and applying knowledge and expertise, often through collaborative networks or partnerships.
- The systematic and intentional process of sharing knowledge and expertise within and between organizations or communities, with the goal of improving outcomes and driving innovation.
Overall, knowledge exchange involves the sharing of knowledge, expertise, and information between individuals, organizations, and communities to build capacity, drive innovation, and improve outcomes.
It is a dynamic and collaborative process that can take many different forms, depending on the specific context and goals of the exchange.
Knowledge Transfer vs Knowledge Exchange
Knowledge transfer and knowledge exchange are two related but distinct concepts in the field of knowledge management. They both involve the sharing of information, expertise, and skills between individuals, groups, or organizations. However, they differ in their focus and the nature of the interaction between the involved parties.
Knowledge Transfer:
- Direction: Knowledge transfer primarily focuses on the one-way flow of information, where one party (the source) imparts knowledge to another party (the recipient). The goal is for the recipient to acquire and apply the knowledge effectively.
- Approach: Knowledge transfer often involves structured processes and methods, such as training sessions, workshops, mentoring, and documentation.
- Objectives: The primary objective of knowledge transfer is to ensure that knowledge is preserved, shared, and used effectively within or between organizations, teams, or individuals. This can help enhance performance, foster innovation, and prevent knowledge loss due to employee turnover.
Knowledge Exchange:
- Direction: Knowledge exchange, on the other hand, emphasizes a more collaborative and reciprocal process, where all parties involved contribute and learn from each other. The exchange of knowledge can happen in multiple directions, creating a dynamic environment for learning and growth.
- Approach: Knowledge exchange often involves more informal and flexible processes, such as open discussions, forums, networking events, and online communities. It encourages the sharing of experiences, ideas, and best practices between participants.
- Objectives: The primary objective of knowledge exchange is to create a collaborative environment that encourages learning, innovation, and the co-creation of knowledge. It fosters a culture of continuous improvement and adaptation by sharing insights, experiences, and expertise across boundaries.
In summary, knowledge transfer is more focused on the one-way flow of information and structured processes, while knowledge exchange emphasizes reciprocal, collaborative interactions and the co-creation of knowledge. Both concepts are important in the field of knowledge management and can be complementary when applied effectively.

Why is Knowledge Exchange Important?
knowledge exchange is important for various reasons, including innovation. These reasons include enhanced decision-making, improved efficiency, support for employee development, building a learning culture, strengthening relationships, managing risks, and bolstering reputation and competitiveness.
Organizations that actively engage in knowledge exchange are often perceived as thought leaders and innovators in their fields. This can enhance their reputation, attract talent, and improve their competitive position in the market.
Knowledge Exchange and Innovation
Knowledge exchange is crucial for innovation because it facilitates the sharing of ideas, experiences, and expertise among individuals, teams, and organizations. This collaborative and reciprocal process can foster creativity and drive innovation in several ways:
Cross-fertilization of Ideas
Knowledge exchange allows individuals and organizations to share and build upon diverse perspectives, experiences, and ideas. This cross-fertilization can lead to new insights, novel solutions, and innovative approaches to solving problems. It supports an innovative culture.
Learning from Others’ Experiences
By exchanging knowledge, organizations and individuals can learn from the successes and failures of others. This can help them avoid common pitfalls, identify best practices, and adapt more quickly to new challenges and opportunities.
Reducing Knowledge Silos
Knowledge exchange helps break down barriers between departments, teams, and individuals, allowing for a more holistic and integrated view of the organization’s knowledge. This can promote greater collaboration and interdisciplinary innovation.
Access to External Knowledge
Knowledge exchange allows organizations to tap into external sources of knowledge, such as partners, customers, and suppliers. This can help organizations stay updated on the latest trends, technologies, and market demands, driving innovation and competitiveness.
Networking and Relationship Building
Knowledge exchange fosters networking and relationship building, which can lead to new partnerships, collaborations, and business opportunities. These connections can provide access to additional resources, expertise, and ideas that can spur innovation. They support the development of collaborative innovation and a thriving innovation ecosystem.
Continuous Improvement
Knowledge exchange encourages a culture of continuous learning and improvement, where organizations and individuals are constantly adapting, refining, and evolving their ideas, products, and processes. This innovation mindset is essential for driving innovation and staying ahead in a rapidly changing world.

Influencing Public Policy
Knowledge exchange influences public policy by facilitating the flow of information, ideas, and expertise between researchers, policymakers, and practitioners. Through this process, evidence-based research findings can inform policy decisions, leading to more effective and targeted interventions.
Additionally, ke activity allows policymakers to learn from the successes and failures of other jurisdictions, fostering the adoption of best practices and innovative approaches. In turn, this contributes to better policy outcomes, addressing societal challenges, and promoting economic growth and well-being.
For a guide on how to run a great knowledge exchange networking event, have a look at my article here.
Universities and Knowledge Exchange
The importance of knowledge exchange for universities can be understood through the following aspects:
Research Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Innovation
Knowledge exchange encourages collaboration among researchers from different disciplines, institutions, and countries. This cross-fertilization of ideas can lead to breakthrough innovations and interdisciplinary research, pushing the boundaries of human knowledge.
It enables research organizations to share ideas, collaborate, and access diverse perspectives. This process fosters innovation, avoids duplication of efforts, and accelerates problem-solving, ultimately leading to improved research results and outcomes, and more impactful discoveries.
Improved Teaching and Learning
Knowledge exchange allows faculty members to share and learn from best practices in teaching and pedagogy. This can lead to more effective teaching methods and improved student outcomes. Students can also benefit from exposure to diverse perspectives and experiences, enhancing their critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Internationalization and Global Partnerships
Universities engage in knowledge exchange by forming partnerships and collaborations with other institutions, businesses, and governments worldwide. These relationships can help universities access new resources, expand their research and teaching capacity, and improve their global reputation.
Community Engagement and Societal Impact
Knowledge exchange enables universities to engage with local, national, and international communities, sharing their expertise and resources to address social, economic, and environmental challenges. This can strengthen the university’s role as a catalyst for positive change and enhance its societal impact.
Knowledge Transfer and Commercialization
Knowledge exchange promotes the transfer of knowledge from universities to industry, enabling the development of new products, services, and technologies. This can generate economic growth, create jobs, and contribute to the overall competitiveness of a region or country.
Attracting Talent and Resources
Universities that actively participate in knowledge exchange can attract high-quality faculty, students, and researchers, as well as funding from public and private sources. This can help institutions maintain their competitive edge in a global higher education landscape.
Lifelong Learning and Professional Development
Knowledge exchange supports the concept of lifelong learning by providing opportunities for faculty, students, and alumni to continuously update their skills and knowledge. This can help individuals stay relevant in their fields and contribute to their professional growth.
Life experience also contributes by providing unique insights, perspectives, and expertise. Individuals with diverse experiences can share their practical wisdom, enriching discussions and enhancing collective understanding. This exchange helps foster innovation, problem-solving, and informed decision-making across various domains.
The ‘Third Mission’ for Universities
Knowledge exchange is essential for universities as it drives research collaboration, improves teaching and learning, fosters internationalization, enhances community engagement, facilitates knowledge transfer, attracts talent and resources, and supports lifelong learning.
By embracing knowledge exchange, universities can enhance their global reputation and contribute more effectively to the advancement of knowledge, innovation, and societal well-being. It is the ‘third mission’ of universities, after the other missions of teaching and research.
The International Association of Universities (IAU)
The International Association of Universities (IAU) is a global organization that fosters cooperation and knowledge exchange among higher education institutions. The IAU facilitates this through several key mechanisms:
- Networking and Collaboration: The IAU brings together universities and higher education institutions from around the world, enabling them to share experiences, best practices, and innovative ideas. By creating opportunities for dialogue and collaboration, IAU helps strengthen the global higher education community.
- Conferences and Events: The IAU organizes international conferences, workshops, and seminars, addressing critical issues in higher education, such as internationalization, sustainable development, and digital transformation. These events provide a platform for academics, policymakers, and practitioners to discuss challenges and explore solutions together.
- Publications and Resources: The IAU produces various publications and resources, including research reports, policy briefs, and guidelines, to inform and support higher education institutions in their decision-making processes. These resources help disseminate knowledge on current trends, challenges, and best practices in the higher education sector.
- Advocacy and Representation: The IAU represents the interests of its members in global policy debates and advocates for the role of higher education in sustainable development, innovation, and societal progress. By engaging in international forums and initiatives, the IAU helps promote knowledge exchange and collaboration across borders.
Knowledge Exchange Concordat
Background to the Concordat
The Knowledge Exchange Concordat is a framework designed to support and enhance the effectiveness of knowledge exchange activities within higher education institutions. It was developed in response to the growing importance of knowledge exchange in higher education.
The Concordat aims to promote good practice and help universities demonstrate their commitment to knowledge exchange, while also identifying areas for improvement.
The concordat is voluntary but encourages institutions to adopt its principles to foster a culture of knowledge exchange and collaboration.
Principles of the Concordat
The Concordat is built around eight guiding principles that outline the key aspects of knowledge exchange. These principles are:
- Developing a clear and ambitious knowledge exchange strategy
- Investing in a skilled and empowered workforce
- Developing strong and productive partnerships
- Inclusive and accessible knowledge exchange
- Recognition and rewards for staff and students involved in knowledge exchange
- Regular evaluation and continuous improvement
- Communicating the value and impact of knowledge exchange
- Ensuring the responsible and ethical conduct of knowledge exchange
Steps for Implementing the Concordat Successfully
Universities can implement the Knowledge Exchange Concordat by following these steps:
- Assess current knowledge exchange practices: Conduct a self-assessment to evaluate the institution’s current activities and identify areas for improvement.
- Develop an action plan: Based on the self-assessment, develop an action plan outlining how the institution will address gaps and enhance knowledge exchange in line with the concordat principles.
- Secure institutional commitment: Obtain support and commitment from senior leadership to ensure that the action plan is fully resourced and embedded in the university’s strategic priorities.
- Engage stakeholders: Involve faculty, staff, students, and external partners in the development and implementation of the action plan to ensure that it is relevant, inclusive, and effective.
- Monitor progress and impact: Regularly review and assess the progress and impact of the action plan, using data and feedback to inform continuous improvement.
- Share good practice and learning: Actively engage with other universities and networks to share experiences, learning, and good practices related to the implementation of the Concordat.
Benefits of the Concordat
Adopting the Knowledge Exchange Concordat can help universities to improve the quality and impact of their knowledge exchange activities, enhance their reputation and competitive advantage, attract funding, partnerships, and talent and foster a culture of collaboration, innovation, and continuous improvement.
What is a Knowledge Exchange Framework?
A Knowledge Exchange Framework (KEF) is a structured system that facilitates the sharing, transfer, and collaboration of knowledge, expertise, and resources among individuals, organizations, or communities. The main objective of a KEF is to enhance innovation, drive economic growth, and improve social outcomes by connecting different stakeholders and promoting the dissemination of valuable knowledge.
The key components of a Knowledge Exchange Framework include:
- Participants: These include individuals, organizations, or communities who are interested in exchanging knowledge or learning from one another.
- Knowledge Assets: These are the pieces of information, expertise, or resources that participants want to share or acquire.
- Platforms or Channels: These are the communication tools or methods that facilitate the exchange of knowledge, such as online forums, workshops, conferences, or collaborative software.
- Processes: These are the activities, steps, or mechanisms that support knowledge exchange, including identification of needs, matchmaking of participants, knowledge sharing, and feedback.
- Metrics and Evaluation: These involve the measurement and assessment of the effectiveness and impact of the knowledge exchange process, which can be used for continuous improvement and to demonstrate the value of the exchange.
A Knowledge Exchange Framework can be implemented across various domains and industries, such as academia, business, government, and non-profit organizations, to foster collaboration, enhance decision-making, and drive innovation.
Examples of Knowledge Exchange Activities
Some examples of knowledge exchange activities include knowledge transfer partnerships, knowledge transfer networks and knowledge exchange networks.
Knowledge Transfer Partnerships and Knowledge Transfer Networks
KTPs (Knowledge Transfer Partnerships) and KTNs (Knowledge Transfer Networks) are UK-based initiatives designed to foster collaboration and knowledge exchange between businesses, academic institutions, and other organizations to promote innovation and drive economic growth. Both initiatives are funded and supported by Innovate UK, the UK’s innovation agency.
KTPs and KTNs play a critical role in promoting innovation and economic growth by connecting businesses with academia and other organizations, and fostering knowledge exchange and collaboration.
KTPs (Knowledge Transfer Partnerships)
A KTP is a government-funded program that brings together a business, an academic institution (such as a university or research institution), and a recent graduate (known as a KTP Associate) to work on a specific project. The aim is to transfer knowledge, expertise, and technology from academia to the business, enabling the development of new products, processes, or services. The KTP Associate works as a project manager, bridging the gap between the business and the academic institution partner organizations, while gaining valuable industry experience. KTPs can last between 12 and 36 months, depending on the project’s scope and objectives.
KTNs (Knowledge Transfer Networks)
KTNs are networks of businesses, academic institutions, and other organizations that facilitate collaboration and knowledge exchange across various industries and sectors. They act as a platform for sharing ideas, best practices, and opportunities among their members, and they organize events, workshops, and conferences to foster networking and learning. KTNs also provide access to funding, resources, and expert advice to help businesses and researchers collaborate on innovative projects. There are multiple KTNs in the UK, each focused on specific sectors or technologies, such as health, materials, energy, or artificial intelligence.
KENs (Knowledge Exchange Networks)
The Knowledge Exchange Network (KEN) is a collaborative platform for professionals, researchers, organizations, and communities. Although there are various KENs with specific focus areas, the general purpose of these networks is to foster the sharing of information, ideas, and best practices.
Here are some key ways KENs facilitate knowledge exchange:
- Online Platforms: KENs typically provide online platforms, such as websites, forums, or social media groups, where members can share resources, engage in discussions, and collaborate on projects. These platforms allow participants to connect, learn from each other, and access valuable information and expertise.
- Webinars and Virtual Events: KENs often organize webinars, workshops, and virtual events that enable members to learn about the latest research, trends, and best practices in their field. These events provide opportunities for networking, knowledge sharing, and professional development.
- Resource Libraries: KENs curate and maintain a library of resources, including articles, reports, case studies, and multimedia content, that members can access to enhance their understanding of specific topics and learn from the experiences of others.
- Collaborative Projects: KENs facilitate collaboration among members by connecting them with potential partners and providing tools for project management and communication. By working together on projects, members can share knowledge, expertise, and resources to achieve common goals.
- Networking Opportunities: KENs provide opportunities for members to build relationships and expand their professional networks, both within and outside their respective fields. These connections can lead to new insights, partnerships, and collaborative initiatives that further promote knowledge exchange.
Overall, Knowledge Exchange Networks play a crucial role by providing an accessible and interactive platform for sharing information, ideas, and best practices, as well as fostering collaboration and networking among members.
An example is the Marine Knowledge Exchange Network.
Intellectual Property (IP)
Intellectual property (IP) ownership in knowledge exchange can be complex, as it involves the sharing and transfer of information, ideas, and expertise between individuals, organizations, or institutions.
Knowledge exchange can occur in various contexts, such as research collaborations, joint ventures, licensing agreements, consultancy services, or educational programs. In each scenario, IP ownership and rights need to be clearly defined and negotiated to ensure that all parties involved are protected and fairly compensated for their contributions.
Here are some general principles and guidelines for IP ownership in knowledge exchange:
Pre-existing IP
Before entering into any agreement or collaboration, it is important to identify and establish the ownership of any pre-existing IP. This includes patents, copyrights, trademarks, and other intellectual property rights that each party brings to the collaboration. In most cases, pre-existing IP remains the property of the original owner unless explicitly agreed otherwise.
Newly Created IP
Intellectual property that is developed during the course of the collaboration needs to be clearly defined and its ownership established. This may involve joint ownership, exclusive or non-exclusive licensing, or assigning the IP rights to one party. The specific terms will depend on the nature of the collaboration, the contributions of each party, and any legal or contractual obligations.
Confidentiality and Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs)
In many knowledge exchange situations, it may be necessary to share confidential information or trade secrets with other parties. To protect the IP rights and interests of each party, it is essential to have a confidentiality or non-disclosure agreement in place. This agreement should outline the specific information that is considered confidential, the obligations of each party to protect the information, and any limitations or restrictions on the use and disclosure of the information.
Publication and Dissemination of Results
Collaboration often involves the generation of new knowledge, and the dissemination of this knowledge may be a key goal of the collaboration. However, it is important to balance the interests of all parties when it comes to publishing or sharing the results. This may involve negotiating terms regarding the timing and extent of publication, authorship and attribution, and any restrictions or limitations on the use of the results for commercial or other purposes.
Contractual Agreements
To ensure clarity and protect the interests of all parties, it is crucial to have a written agreement in place that outlines the terms and conditions of the knowledge exchange, including the ownership and management of any intellectual property rights. This agreement should be negotiated and agreed upon before the commencement of the collaboration and should be reviewed and updated as needed throughout the course of the project.
Summary
In conclusion, IP ownership in knowledge exchange can be complex and requires careful consideration and negotiation to ensure that the rights and interests of all parties involved are protected. It is advisable to consult with legal experts or IP professionals when entering into any agreements or collaborations to ensure that the appropriate measures are in place to safeguard the intellectual property rights of all parties.
Knowledge Exchange Organizations
There are several leading organizations in the world that promote knowledge sharing, collaboration, and innovation across a variety of sectors.
These organizations work to promote knowledge exchange in a variety of ways, such as facilitating collaboration between researchers and practitioners, promoting the sharing of best practices, and supporting the development of new ideas and innovations.
Through their efforts, these organizations are helping to build a more connected and collaborative world where knowledge can be shared and leveraged for the benefit of all.
Here are some of the most prominent of these organizations:
1. World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
WIPO helps universities and research organizations to find wider uses for their discoveries and innovations. It provides legal services, professional training, materials and resources, especially concerned with intellectual property (IP).
2. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
Promoting open access to information and knowledge
UNESCO supports knowledge exchange through a variety of initiatives and programs aimed at promoting collaboration, sharing of best practices, and building capacity in various fields as follows:
UNESCO supports the development of open access policies and initiatives that make research and knowledge freely available to all. This includes promoting open access to scientific publications and data, as well as advocating for the use of open educational resources.
Promoting collaboration and partnership
UNESCO supports the establishment of networks and partnerships between individuals, organizations, and institutions to promote collaborative research. This includes supporting the establishment of research networks, partnerships between universities and industries, and collaborations among cultural institutions.
Supporting capacity building
UNESCO supports the development of human capacity through training and education programs that help individuals and communities to acquire the understanding and skills necessary to participate in knowledge exchange and innovation. This includes supporting the development of science and technology education programs, as well as promoting the use of new and emerging technologies for learning and knowledge sharing.
Advocating for knowledge exchange policies and practices
UNESCO promotes policies and practices that support innovation, including open science policies, intellectual property policies, and policies that promote the use of new and emerging technologies.
3. World Bank
The World Bank plays a significant role in facilitating knowledge exchange globally, particularly in the context of international development. As an international financial institution, the World Bank not only provides financial support to developing countries but also actively engages in sharing knowledge, expertise, and best practices to address critical development challenges. This is done through several key initiatives and platforms:
Knowledge Products
The World Bank produces a wide range of research publications, policy papers, data, and analytical tools that provide insights and guidance on various development topics, such as poverty reduction, education, health, and infrastructure. These resources are made available to policymakers, practitioners, and researchers worldwide, enabling them to learn from global experiences and adapt successful strategies to their local contexts.
Technical Assistance and Capacity Building
The World Bank provides technical assistance and capacity-building support to developing countries, helping them strengthen their institutional and human resources. This often involves sharing knowledge and expertise through training programs, workshops, and advisory services, which enable countries to enhance their skills and capabilities in critical areas like public financial management, environmental management, and governance.
South-South Knowledge Exchange
The World Bank actively promotes South-South knowledge exchange, where developing countries learn from one another’s experiences and best practices. This is done through various mechanisms, such as knowledge forums, study tours, and peer-to-peer learning networks, where policymakers and practitioners from different countries can share their insights, challenges, and solutions on a range of development issues.
Partnerships and Collaborative Platforms
The World Bank collaborates with a wide range of partners, including governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector, to facilitate joint learning. These partnerships often involve the creation of collaborative platforms, such as knowledge hubs, online communities, and global networks, which enable stakeholders to share information, resources, and expertise on specific development topics.
Innovation and Technology
The World Bank supports the development and dissemination of innovative solutions and technologies that can help address development challenges more effectively. This includes promoting the use of digital tools and platforms for knowledge sharing. These platforms include online portals, mobile applications, and e-learning resources. In addition they support initiatives that foster innovation, entrepreneurship, and the application of cutting-edge technologies in development.
4. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is an international organization. It plays a vital role in facilitating knowledge exchange among its member countries and partners.
Comprising 38 member countries, the OECD aims to promote policies that improve economic and social well-being globally. OECD countries and Key Partners represent about 80% of world trade and investment.
The organization fosters collaboration, sharing best practices, and providing a platform for dialogue on a wide range of policy issues.
Research and Analysis
The OECD conducts extensive research and analysis on various economic, social, and environmental issues. These range from macroeconomic policy to education, health, and sustainable development. By producing comprehensive reports, policy briefs, working papers, and statistical databases, the OECD provides valuable insights and evidence-based recommendations to policymakers and stakeholders. This wealth of knowledge helps inform decision-making and fosters the adoption of effective policies and practices across countries.
Policy Dialogue
The OECD serves as a forum for policy dialogue and exchange. Member countries and partners can discuss pressing challenges, share experiences, and identify innovative solutions. Regular meetings, workshops, and conferences enable representatives from governments, academia, businesses, and civil society to engage in constructive discussions.
Peer Reviews
The OECD conducts peer reviews to assess and evaluate the performance of its member countries in various policy areas. These reviews involve a rigorous examination of a country’s policies, practices, and institutions, followed by recommendations for improvement. By engaging in a transparent and collaborative process, countries can learn from one another’s experiences and adopt best practices to enhance their policy outcomes.
Capacity Building and Technical Assistance
The OECD provides capacity building and technical assistance to support countries in implementing effective policies and reforms. Through training programs, advisory services, and the sharing of technical expertise, the OECD helps strengthen the capabilities of national institutions and develop human resources. This support enables countries to better design and implement policies that address their specific challenges and needs.
Global Partnerships and Networks
The OECD collaborates with a diverse range of policy makers, international organizations, regional bodies, and non-member countries. It promotes cooperation on global policy challenges. By establishing partnerships and networks, the OECD can broaden its reach and impact. This allows countries to learn from a wider array of experiences and perspectives.
Knowledge Exchange Conferences and Events
These conferences and events offer valuable opportunities for professionals, academics, and policymakers to learn from one another. In addition, it helps them to stay informed about the latest trends and developments in their respective fields.
European Conference on Innovation and Entrepreneurship (ECIE)
This international conference brings together researchers, academics, policymakers, and practitioners to discuss and exchange ideas on innovation and entrepreneurship. Participants explore the latest research, trends, and best practices in these fields to foster collaboration and drive economic growth.
Knowledge Management World (KMWorld)
KMWorld is a leading conference on knowledge management, content management, and information management. The event features presentations, workshops, and panel discussions, addressing topics such as knowledge sharing, collaboration, and organizational learning.
European Conference on Knowledge Management (ECKM)
ECKM is a prominent academic conference focused on knowledge management, innovation, and intellectual capital. The event attracts scholars, practitioners, and policymakers from various disciplines to share their research, insights, and experiences.
Open Repositories Conference (OR)
OR is an annual conference. It explores the challenges and opportunities of open access, open data, and open knowledge in the digital age. Participants from academia, libraries, archives, and industry discuss the latest developments in repository technologies, policies, and practices.
International Conference on Communities and Technologies (C&T)
C&T is a biennial conference that explores the intersection of communities, technology, and knowledge exchange. The event addresses topics such as social media, digital collaboration, and online communities. It has a focus on the role of technology in fostering knowledge sharing and community engagement.
Praxis Auril Conference
The Praxis Auril Conference is an annual event. It brings together professionals, researchers, and policymakers involved in knowledge exchange, technology transfer, and innovation management. The conference focuses on fostering collaboration between academia and industry. It promotes the commercialization of research, and maximizing the societal and economic impact of knowledge. Attendees can expect engaging presentations, panel discussions, and workshops on best practices, policy developments, and case studies. The event provides an excellent opportunity for networking, professional development, and staying up-to-date with the latest trends and challenges.
Resources and Literature
Here are some related sources and literature:
- Nonaka, I., & Takeuchi, H. (1995). The Knowledge-Creating Company: How Japanese Companies Create the Dynamics of Innovation. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Wenger, E. (1998). Communities of Practice: Learning, Meaning, and Identity. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Polanyi, M. (1966). The Tacit Dimension. New York: Doubleday.
- Davenport, T. H., & Prusak, L. (1998). Working Knowledge: How Organizations Manage What They Know. Boston: Harvard Business School Press.
- Fazey, I. et al. (2013). “Knowledge Exchange: a Review and Research Agenda for Environmental Management.” Environmental Conservation 40(1):19–36.

