Posted in Auditing Tips, Blog, Create, Design Thinking, Facilitation, Innovation, Virtual Facilitation by Jo North
History of the creative problem-solving process
What is creative problem-solving?
Creative problem-solving is a step-by-step process designed to spark creative thinking and innovative solutions for purposeful change. It is sometimes abbreviated to “CPS”.
The creative problem-solving process is at the root of other contemporary creativity and innovation processes, such as innovation sprints and design sprints or design thinking. These methods have been adapted and repackaged into the fundamental principles of creative problem-solving.
Here’s a quick overview of how the creative problem-solving process has developed over time.
Creative problem solving: Osborn
The originator of the creative problem-solving process, Alex Osborn, was a founding partner of an American advertising agency. He published a seven-stage creative problem solving-process (Osborn, 1952).
Osborn’s seven-stage process
- Orientation
- Preparation
- Analysis
- Hypothesis
- Incubation
- Synthesis
- Verification
Further publications (Osborn 1953; 1957; 1967) raised general awareness of the method. Osborn also launched the concept of ‘brainstorming’ into common practice and language for the first time.
Later, Osborn refined his process to contain only three stages (Osborn, 1967).
Osborn’s three-stage process
- Fact-finding
- Idea-finding
- Solution-finding
Osborn-Parnes process
Osborn met and began to collaborate with Sidney Parnes, who continued to develop Osborn’s work after he died, to create a five-stage process (Parnes, 1967a; 1967b).
This five-step Creative Problem-Solving Process was developed with the educational purpose of enabling students to develop their personal creativity.
This five-stage process was used in a range of education programs in the US, and became known as the Osborn-Parnes Creative Problem-Solving Model (Parnes, 1967a; 1967b).
The five steps are:
- Fact-finding
- Problem-finding
- Idea-finding
- Solution-finding
- Acceptance-finding
Isaksen and Treffinger creative problem-solving model
Isaksen & Treffinger’s Creative Problem Solving: The basic course (1985) added a specific “Mess-Finding” stage onto the beginning of the Osborn-Parnes CPS principles. The course also included more specific guidelines for the convergent thinking elements of the process.
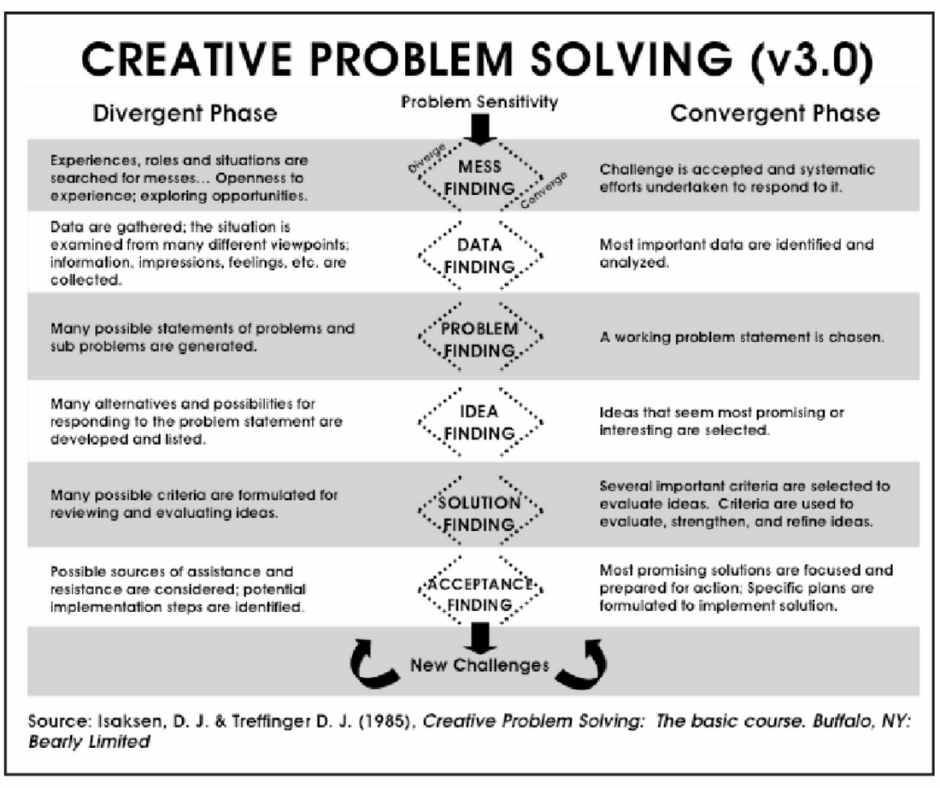
Through the 1980s and 1990s, Isaksen and Treffinger continued to refine the model:
- Making it more usable, by breaking the process up into more manageable steps (version 4.0)
- Taking a more descriptive approach, to make the process and each of its steps clearer. They also improved guidance on planning (version 5.0)
- Including task appraisal and process planning to form a “Planning Your Approach” stage (versions 6.0 and 6.1)
By 2000, their CPS Version 6.1™ system comprised four components and eight stages.
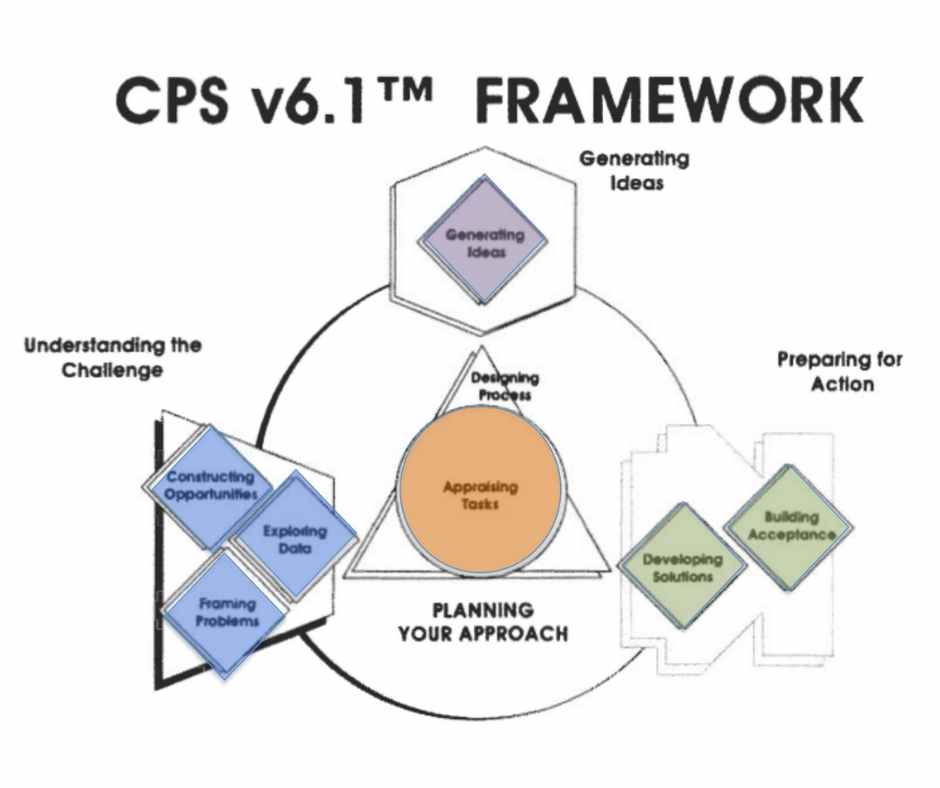
Creative Problem-Solving Thinking Skills Model (TSM)
A more recent development of the creative problem-solving process is the Creative Problem Solving Thinking Skills Model (TSM) by Puccio, Mance & Murdock, 2011.
The Creative Problem-Solving TSM model has three key stages. These are:
- Clarification
- Transformation
- Implementation
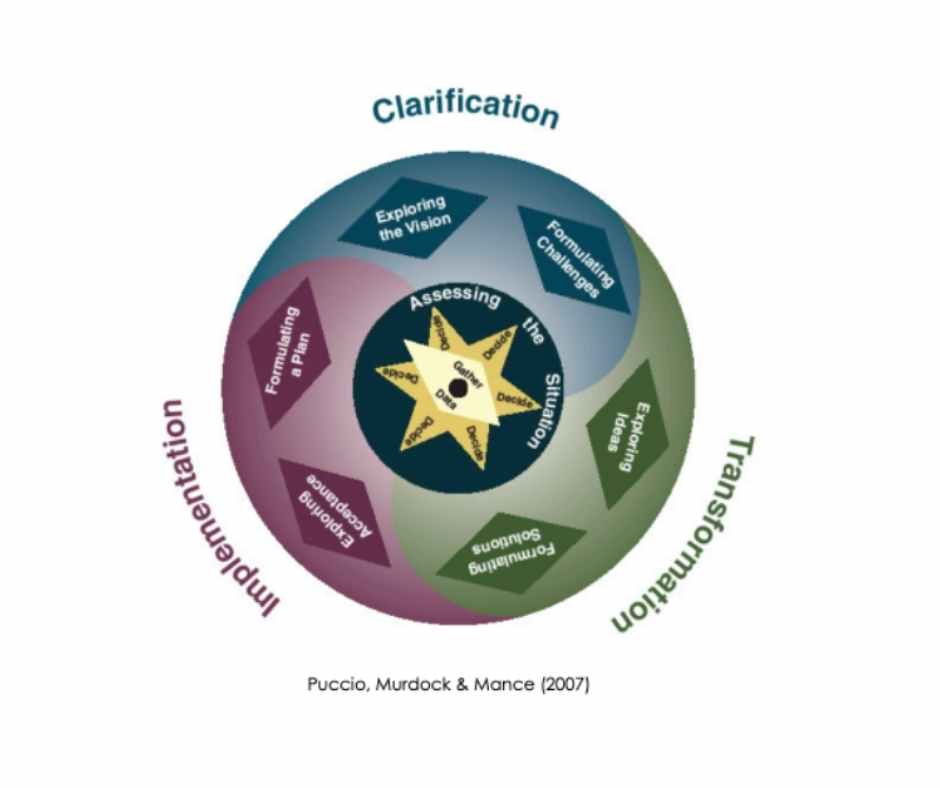
It also contains six specific steps:
- Exploring the vision
- Formulating challenges
- Exploring ideas
- Formulating solutions
- Exploring acceptance
- Formulating a plan
Divergent and convergent thinking
Each step includes divergent and convergent thinking phases.
- Divergent thinking means a broad search for many diverse and novel ideas.
- Convergent thinking means selecting options through an informed evaluation of alternatives.
There is one executive step, “assessing the situation”, at the heart of the model. “Assessing the situation” guides all the steps. This means that at every stage, it’s a good idea to step into the circle, when you need to, to gather more data and assess the situation.
By implementing the skills incorporated within this model, organizations can develop their teams to deliver more creative and innovative results.
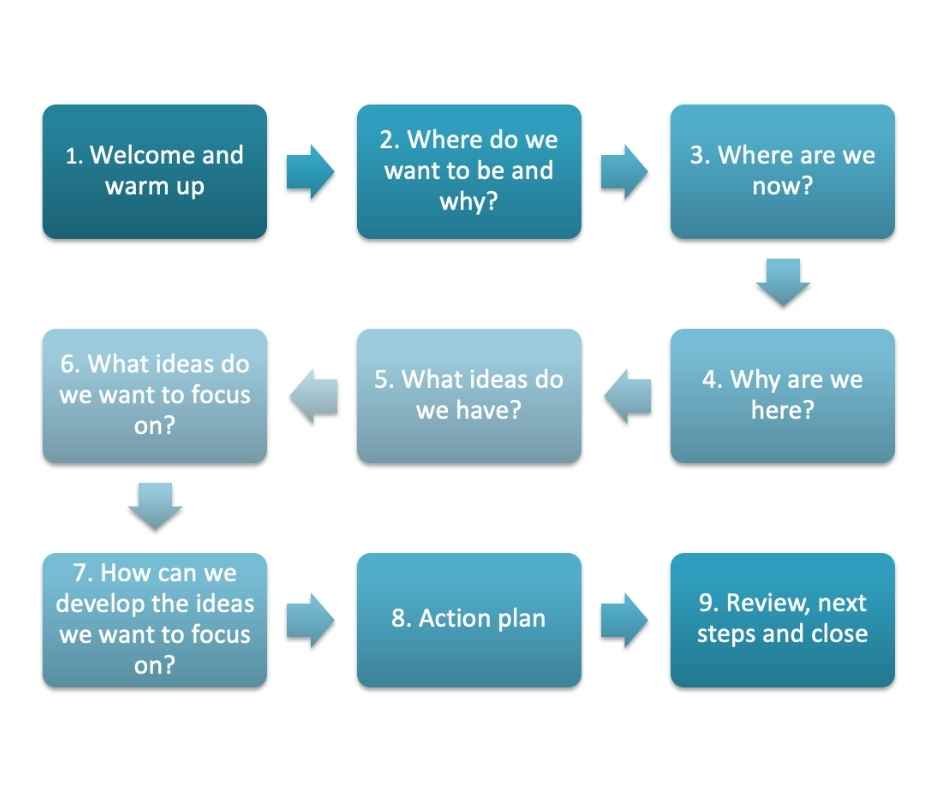
Creative problem-solving journey from The Big Bang Partnership
Over the last 12 years, we have developed our own creative problem-solving journey which we use in our clients’ workshops. We also train facilitators to use our method.
We design and lead workshops online and in-person.
We have built our approach based on academic research and evidence, combined with real experience of working with literally thousands of people in a huge range of diverse organisations around the world.
Our approach is massively facilitator and participant-friendly. It delivers great results every time. It’s also brilliantly flexible because we curate activities for each individual workshop from over 300 creative problem-solving techniques. We have adapted from some of the classic CPS techniques, and invented our own.
We also make sure that we use divergent and convergent thinking activities at just the right time. Plus, we make the whole experience enjoyable as well as productive for everyone.
Need some help with your creative problem-solving workshop?
Here are The Big Bang Partnership we are expert facilitators of creative problem solving workshops. Please do comment or email us if you would like any further tips or advice, or if you’d like to explore having us design a facilitate a workshop for you.

